Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform have revolutionized the way we manage cloud infrastructure. One of Terraform’s key features is state management, which keeps track of your infrastructure’s current state and ensures that changes are applied consistently. Proper state management is critical for avoiding conflicts, maintaining
consistency, and enabling collaboration across teams.
In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of state management in Terraform, how to use workspaces for managing multiple environments, and how to integrate Terraform with Azure DevOps for streamlined CI/CD workflows. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to manage Terraform state effectively and automate your infrastructure deployments.
What is Terraform State?
Terraform uses a state file (terraform.tfstate) to store information about your infrastructure. This file acts as a source of truth for Terraform, allowing it to:
- Track the resources it manages.
- Detect changes between your configuration and the actual infrastructure.
- Plan and apply updates efficiently.
By default, Terraform stores the state file locally, but for team collaboration and production environments, it’s recommended to use a remote backend like Azure Blob Storage, AWS S3, or HashiCorp Consul.
Why is State Management Important?
Proper state management ensures:
- Consistency: Terraform knows the exact state of your infrastructure, preventing unintended changes.
- Collaboration: Remote state storage allows multiple team members to work on the same infrastructure without conflicts.
- Environment Isolation: Workspaces enable you to manage multiple environments (e.g., dev, staging, production) with separate state files.
Using Terraform Workspaces for Environment Management
Terraform workspaces allow you to manage multiple environments (e.g., dev, staging, prod) within the same configuration. Each workspace has its own state file, making it easy to isolate environments.
Creating and Using Workspaces
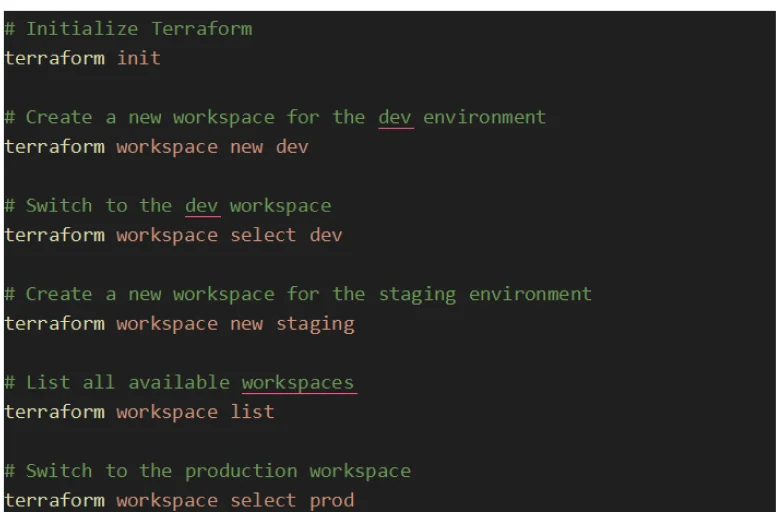
Using Workspaces in Configuration
You can use the terraform.workspace variable to dynamically configure resources based on the active workspace. For example:
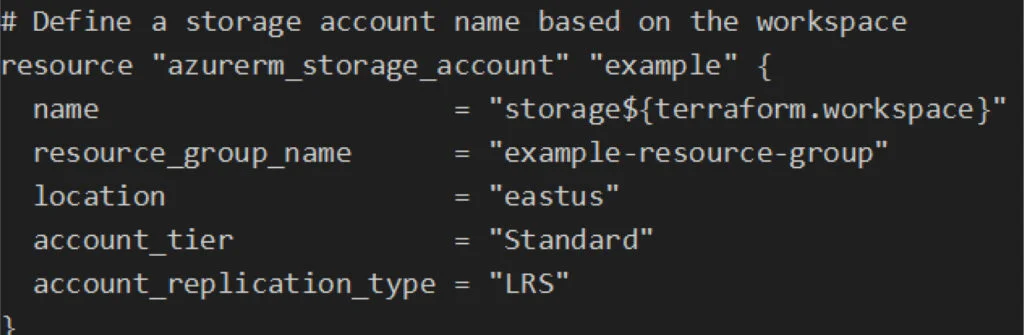
In this example, the storage account name will include the workspace name (e.g., storagedev, storagestaging, storageprod).
Integrating Terraform with Azure DevOps
Integrating Terraform with Azure DevOps enables you to automate infrastructure deployments as part of your CI/CD pipeline. Here’s how to set it up:
1. Store Terraform State in Azure Blob Storage
To enable collaboration, configure Terraform to use Azure Blob Storage as the remote backend:
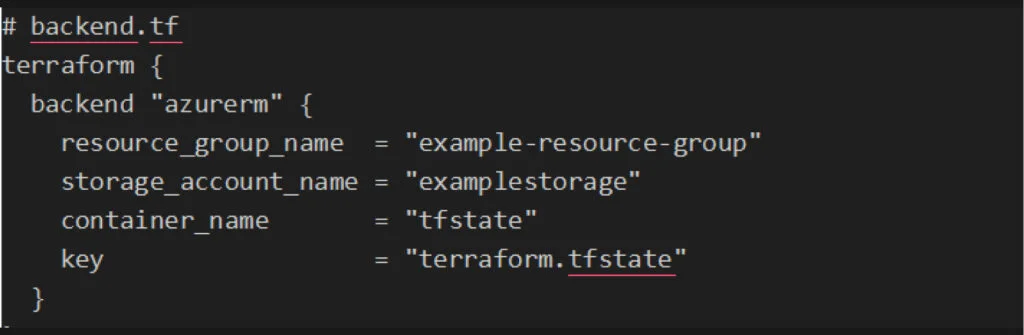
Run the following command to initialize the backend:
terraform init
2. Create a Terraform Pipeline in Azure DevOps
Here’s an example of an Azure DevOps pipeline (azure-pipelines.yml) for deploying infrastructure using Terraform:
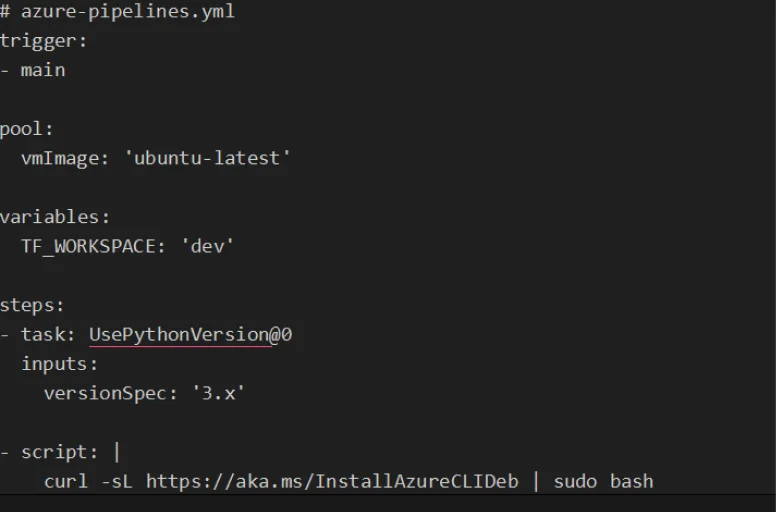
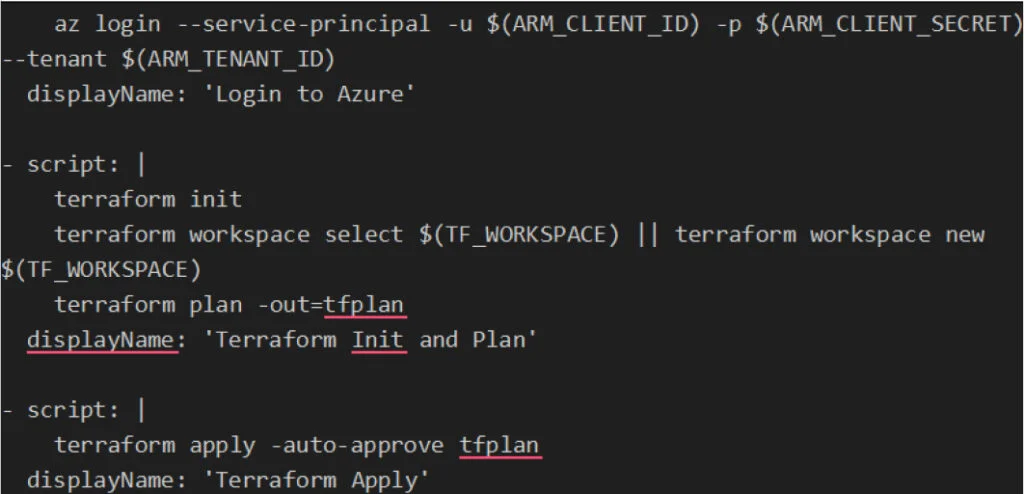
3. Secure Your Pipeline
Store sensitive information like Azure credentials
(ARM_CLIENT_ID, ARM_CLIENT_SECRET, ARM_TENANT_ID) in Azure DevOps Pipeline Secrets to keep them secure.
Best Practices for Terraform State Management
- Use Remote Backends: Always use a remote backend for production environments to enable collaboration and ensure state consistency.
- Lock State Files: Use state locking to prevent multiple users from modifying the state simultaneously. Most remote backends, like Azure Blob Storage, support state locking.
- Isolate Environments: Use workspaces or separate backends for different environments to avoid accidental changes.
- Version Control: Store your Terraform configuration files in a version control system like Git to track changes and enable rollbacks.
Why Choose Us for Terraform and Azure DevOps Integration?
Managing Terraform state and integrating it with Azure DevOps can be complex, especially for large-scale environments. At CloudsUP Solutions, we specialize in:
- Setting up Terraform for enterprise-grade infrastructure.
- Configuring secure and scalable remote backends.
- Automating deployments with Azure DevOps pipelines.
- Providing tailored solutions for your unique business needs.
Whether you’re just starting with Terraform or looking to optimize your existing workflows, our team of experts is here to help. Contact us today to streamline your infrastructure management and unlock the full potential of Terraform and Azure DevOps.
Conclusion
State management is a critical aspect of using Terraform effectively. By leveraging workspaces for environment isolation and integrating Terraform with Azure DevOps, you can automate your infrastructure deployments while maintaining consistency and security. With the right practices and tools, you can simplify infrastructure management and focus on delivering value to your business.
If you’re ready to take your Terraform workflows to the next level, let us help you implement best practices and seamless integrations. Together, we can build a robust and scalable infrastructure for your organization!
